Elevator pitch
Formal schooling increases earnings and provides other individual benefits. However, societal benefits of education may exceed individual benefits. Research finds that higher average education levels in an area are correlated with higher earnings, even for local residents with minimal education. Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) graduates appear to generate especially strong external effects, due to their role in stimulating innovation and economic growth. Several strategies to test for causality find human capital externalities do exist.
Key findings
Pros
Economic theory suggests that there are external benefits of education, such as learning from peers and synergies in problem-solving.
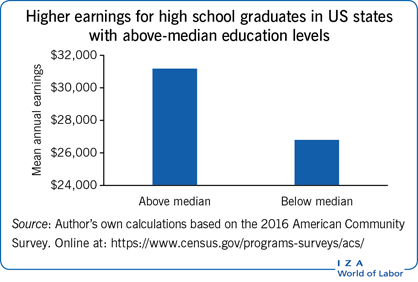
Empirical studies find a positive correlation between higher local education levels and higher earnings.
Human capital externalities are strongly linked to increases in the stock of college graduates in an area.
Externalities associated with higher local education levels benefit all workers, especially less educated workers.
Externalities appear to be particularly strong from STEM graduates.
Cons
Positive correlation between high local education levels and earnings of other workers may result from highly educated workers moving to areas that already pay high wages.
There may be unobservable characteristics that increase both local education levels and wages.
Policies to raise education levels by encouraging highly educated immigrants could adversely affect some native workers.
Human capital may increase the local price of non-tradable goods and services such as housing, to the detriment of the less educated.
Local education levels may increase inequality if more educated workers benefit more.