Elevator pitch
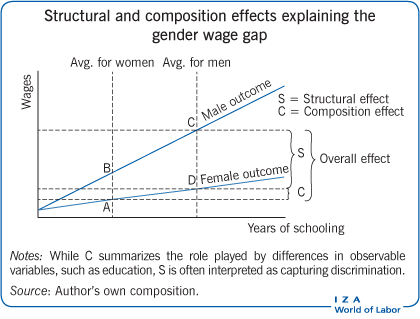
Differences in wages between men and women, white and black workers, or any two distinct groups are a controversial feature of the labor market, raising concern about discrimination by employers. Decomposition methods shed light on those differences by separating them into: (i) composition effects, which are explained by differences in the distribution of observable variables, e.g. education level; and (ii) structural effects, which are explained by differences in the returns to observable and unobservable variables. Often, a significant structural effect, such as different returns to education, can be indicative of discrimination.
Key findings
Pros
Potential discrimination in the labor market can be analyzed using decomposition methods.
Decomposition methods point to factors that are relevant to explain wage differentials, such as differences in educational attainment or college premia between groups.
Policymakers aiming to reduce inequality between two distinct groups in the labor market can be guided by decomposition results.
Decomposition methods are easily implemented because they are regression based and offered by most statistical software.
Cons
Decomposition methods rely on strong assumptions that are not testable and may not hold in the real world.
Decomposition results are sensitive to the choice of reference group, making it harder to measure precisely composition and structural effects.
It is not possible to determine causal interpretation in general from decomposition results because one cannot change an individual's identity group.
Detailed decomposition results are sensitive to the choice of the omitted categorical variable.