Elevator pitch
Unemployment insurance can be an efficient tool to provide protection for workers against unemployment and foster formal job creation in developing countries. How much workers value this protection and to what extent it allows a more efficient job search are two key parameters that determine its effectiveness. However, evidence shows that important challenges remain in the introduction and expansion of unemployment insurance in developing countries. These challenges range from achieving coverage in countries with high informality, financing the scheme without further distorting the labor market, and ensuring progressive redistribution.
Key findings
Pros
Unemployment insurance can increase the formalization of jobs; in turn, formal jobs may become more valued by workers, and it enables a more efficient job search.
Unemployment insurance can be a better tool to provide income support during unemployment than other instruments, e.g. severance payments.
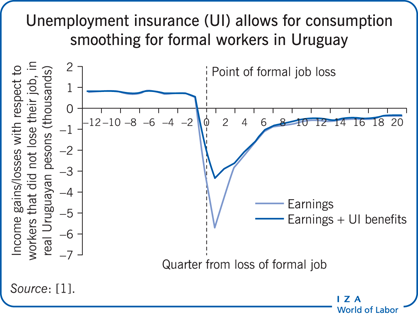
Evidence shows that, even in developing countries, unemployment insurance facilitates consumption smoothing.
Cons
Unemployment insurance coverage will be low in countries with a large informal sector and will probably not cover those most in need.
In countries with high levels of informality and worker turnover, unemployment insurance may transfer resources from low-income to high-income workers.
Moral hazard concerns are more pernicious in countries with high informality, as workers can claim benefits and keep working informally.
There is no evidence that job seekers receiving unemployment insurance find better (formal) jobs.