Elevator pitch
People who are unable to maintain the same standard of living as others around them experience a sense of relative deprivation that has been shown to reduce feelings of well-being. Relative deprivation reflects conditions of worsening relative poverty despite striking reductions in absolute poverty. The effects of relative deprivation explain why average happiness has been stagnant over time despite sharp rises in income. Consumption taxes on status-seeking spending, along with official and traditional sanctions on excess consumption and redistributive policies may lessen the negative impact of relative deprivation on well-being.
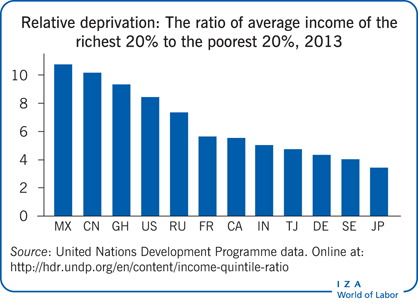
Key findings
Pros
Strong evidence finds a negative impact of relative deprivation on both objective and subjective dimensions of well-being.
Relative deprivation offers a plausible explanation for the paradox that average happiness has remained constant or even fallen despite sharp rises in income.
Psychological services and redistributive policies tailored to people experiencing relative deprivation may improve well-being.
Visibility-based consumption taxes and community sanctions may promote well-being by curbing status-seeking spending driven by relative deprivation.
Relative deprivation reflects relative poverty and complements measures of inequality.
Cons
Psychological services, community-based activities, and redistributive policies may draw attention to a person’s low status and increase relative deprivation.
Studies of relative deprivation assume either external comparisons with richer counterparts or internal comparisons with a person’s past or future self without formally testing the importance of those reference groups.
The true reference group is rarely known, which likely biases measures of relative deprivation.
Few results of relative deprivation studies are directly comparable across studies, and the results are not generalizable to a larger population.