Elevator pitch
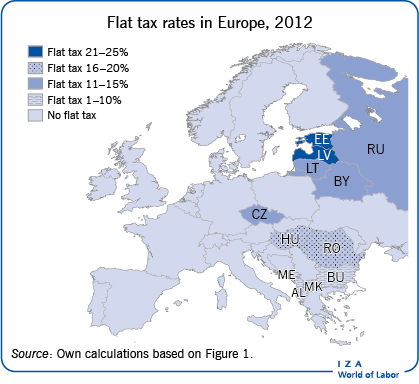
The potential economic outcomes resulting from a flat rate of income tax have been the subject of an ongoing academic and political debate. Many observers have suggested that the introduction of a flat tax would be beneficial for a country’s economy, having a positive influence on the labor market and the gross domestic product by enhancing incentives to work, save, invest, and take risks. A flat tax also significantly simplifies income taxation which increases tax compliance and reduces tax planning, avoidance, and evasion. However, despite flat taxes being on the political agenda in many countries, in practice their implementation has mostly been restricted to the transition economy countries of Eastern Europe. There is no one single flat tax system in place in these countries though; one rate does not fit all.
Key findings
Pros
Flat tax systems are likely to increase labor supply and employment.
Flat tax systems can lead to a simplification of the tax system.
Lower administrative and compliance costs can result from flat tax systems.
Cons
Flat tax systems are likely to lead to redistribution at the expense of the middle class.
Redistribution might cause political opposition.
Flatness of the tax schedule itself is not necessary for the positive effects of tax reform.