Elevator pitch
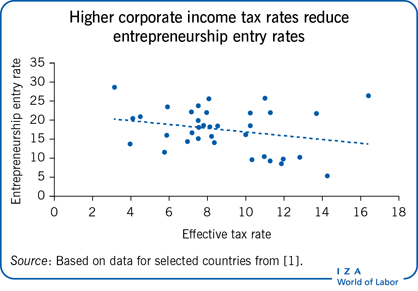
Corporate income taxation influences the quantity and type of entrepreneurship, which in turn affects economic development. Empirical evidence shows that higher corporate income tax rates reduce business density and entrepreneurship entry rates and increase the capital size of new firms. The progressivity of tax rates increases entrepreneurship entry rates, whereas highly complex tax codes reduce them. Policymakers should understand the effects and underlying mechanisms that determine how corporate income taxation influences entrepreneurship in order to provide a favorable business environment.
Key findings
Pros
Corporate income tax rates have a statistically and economically significant influence on entrepreneurship.
The relationship between corporate income taxes and entrepreneurship is stronger than the relationship between other taxes and entrepreneurship.
High effective corporate income tax rates increase the capital size of new firms, thereby enhancing their chances of survivability (“entry barrier effect”).
High levels of corporate income tax progressivity increase entrepreneurship entry rates (“tax progressivity effect”).
Cons
High statutory and high effective corporate income tax rates reduce business density and entrepreneurship entry rates (“tax level effect”), particularly for innovative and high-quality entrepreneurship (“prize reducing effect”).
Reductions in the corporate income tax rate may only affect entrepreneurship rates below a certain threshold tax level.
Corporate income tax rate reductions are more effective at promoting entrepreneurship in countries with higher-quality accounting standards.
Highly complex corporate income tax codes reduce entrepreneurship entry rates (“tax code complexity effect”).
High corporate income tax rates increase the size of the informal sector.