Elevator pitch
It is not possible for a formal employment contract to detail everything an employee should do and when. Informal relationships, in particular trust, allow managers to arrange a business in a more productive way; high-trust firms are both more profitable and faster growing. For example, if they are trusted, managers can delegate decisions to employees with confidence that employees will believe the promised rewards. This is important because employees are often better informed than their bosses. Consequently, firms that rely solely on formal contracts will miss profitable opportunities.
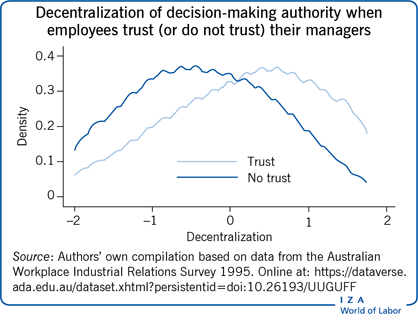
Key findings
Pros
Formal employment contracts are incomplete, necessitating informal agreements to fill the gaps; these informal agreements rely on two-way trust between managers and employees.
Trust comes from individual relationships between an employee and their managers, managerial reputation, and social norms.
Trust allows for more effective task allocation and organizational structures, which can allow firms to better utilize employees’ knowledge and skills, aiding profitability.
Competition in the product market can engender higher levels of trust within organizations, as competition spurs firms to be more productive.
Cons
Market downturns can cause trust to be broken, as managers find it harder to keep past promises in tough times.
External negative shocks mean that trust tends to be lost over time, rather than earned.
Labor mobility makes trust more difficult; shorter employment relationships reduce the reputational costs to managers from breaking their word.
Trust is difficult to manage in organizations because it is the combination of social norms, managerial practices, and individual relationships.