Elevator pitch
Canada, the US, and most Western countries are looking to STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) immigrants to boost innovation and economic growth. Canada in particular has welcomed many STEM immigrants over the past quarter of a century. In the US, there is an ongoing debate about whether the H–1B visa program is being used effectively to attract more STEM immigrants. Interestingly, significant differences exist between the two countries in earnings and likely the innovation activity of highly educated immigrants, which highlights the likely role of immigration policy in determining such outcomes.
Key findings
Pros
Immigration leads to a large supply of highly educated STEM workers in some countries, such as Canada and the US.
Highly educated immigrants contribute disproportionately to patent filing activity in the US and perhaps other countries largely due to the high proportion educated in STEM fields.
In the US, highly educated immigrants working in STEM jobs have a relatively small entry earnings gap with the native born, and “catch up” to the native born very quickly.
Cons
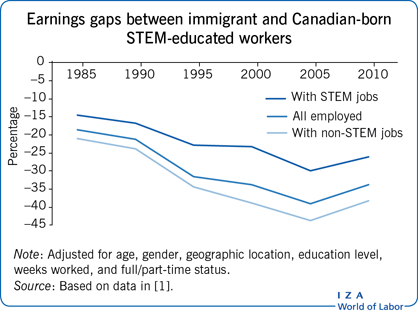
The earnings gap between highly educated immigrants and native STEM employees is much larger in some countries, like Canada, than in others, namely the US.
STEM-educated immigrants who do not find STEM jobs can face very poor economic outcomes, as observed in Canada.
Economic and possibly innovation outcomes are much more positive for STEM immigrants educated in Western developed nations than in developing countries.