Elevator pitch
Despite declining bargaining power, unions continue to generate a wage premium. Some feel collective bargaining has had its day. Politicians on both sides of the Atlantic have recently called for the removal of bargaining rights from workers in the name of wage and employment flexibility, yet unions often work in tandem with employers for mutual gain based on productivity growth. If this is where the premium originates, then firms and workers benefit. Without unions bargaining successfully to raise worker wages, income inequality would almost certainly be higher than it is.
Key findings
Pros
Trade unions maintain and improve workers’ terms and conditions through bargaining with employers.
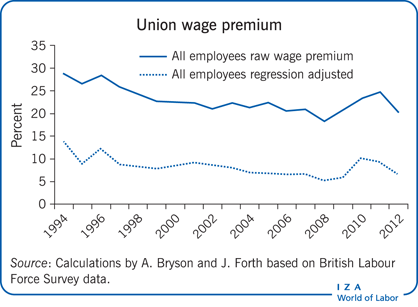
Workers organized in trade unions benefit from higher wages—the so-called union wage premium.
Union bargaining also results in a fringe benefits premium for covered workers.
Trade unions reduce wage inequality.
The counter-cyclical wage premium helps to maintain the real wages of covered workers.
Cons
Trade unions restrict employment flexibility.
Trade unions prevent markets from clearing.
By standardizing wages across regions, unions distort labor supply.
Trade unions harm businesses if the return for additional wages is low.
If the premium comes at the expense of normal profits, this can damage firms and employment growth.