Elevator pitch
Although coverage of collective bargaining agreements has been declining for decades in most countries, it is still extensive, especially in non-Anglo-Saxon countries. Strong unions may influence firms' incentives to invest in capital, particularly in sectors where capital investments are sunk (irreversible), as in research-intensive sectors. Whether unions affect firms' investment in capital depends on the structure and coordination of bargaining, the preference of unions between wages and employment, the quality of labor-management relations, the structure of corporate governance, and the existence of social pacts, among other factors.
Key findings
Pros
By negotiating higher wages, unions may induce firms to reduce employment and substitute capital for labor.
In a strategic environment with bargaining over both wages and employment, greater union power may increase investment in research and development and thus innovation.
Where long-term labor contracts are common, unions may commit in advance not to appropriate rents from investment.
Positive labor relations, the existence of social pacts, and codetermination may boost investment.
If a union expects substantial gains from an innovation, it will bargain for high research and development expenditures when its power increases.
Cons
By raising wage demands after contract negotiation, unions may seize returns on capital and impede investment in capital.
The reduction in investment is larger when capital investment is sunk, as in research-intensive industries.
As long as the returns to capital are appropriable, firms react to union power by reducing both physical capital and research and development expenditures.
Unions have a negative effect on research and development investment in the US, but this effect is not found in other countries.
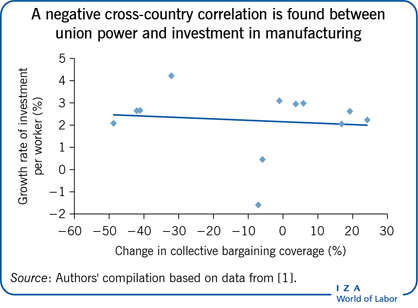
Cross-country evidence shows significant negative effects of unions on investment, especially in research-intensive sectors.