Elevator pitch
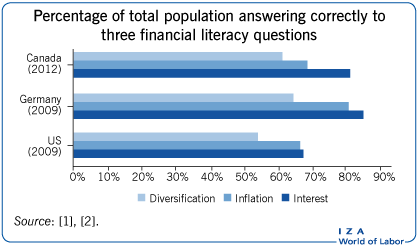
The level of financial literacy in developed countries is low and contributes to growing wealth inequality. Benefits from increasing the level of financial literacy include more effective saving for retirement and better debt management. However, there are significant costs in terms of time and money of acquiring financial literacy, which imply that the net value of acquiring financial literacy is heterogeneous in the population. This potentially makes designing effective interventions difficult.
Key findings
Pros
Financial literacy is associated with better financial outcomes, such as more efficient saving and better debt management; in some cases the relationship is shown to be causal.
Differences in financial literacy may amplify wealth inequality, so early interventions to provide financial literacy may reduce wealth inequality.
Financial education in schools has been shown to have positive effects on financial behaviors.
Cons
Delegating financial decisions to others could, in some circumstances, substitute for the need for higher financial literacy.
Policy-driven behavioral interventions designed to “nudge” workers into taking certain actions may only raise well-being where workers are already financially literate; however, they may be better suited to address inaction and other behavioral biases that do not result from low financial literacy.
Targeting those most in need of financial literacy may be difficult because the costs and benefits of financial knowledge are heterogeneous and thus “universal knowledge” may not be desirable.