Elevator pitch
Public attitudes toward immigration play an important role in influencing immigration policy and immigrants’ integration experience. This highlights the importance of a systematic examination of these public attitudes and their underlying drivers. Evidence increasingly suggests that while a majority of individuals favor restrictive immigration policies, particularly against ethnically different immigrants, there exists significant variation in these public views by country, education, age, and so on. In addition, sociopsychological factors play a significantly more important role than economic concerns in driving these public attitudes and differences.
Key findings
Pros
Recent surveys suggest that the majority of people support relatively restrictive immigration policies and would like to see a decrease in the number of immigrants.
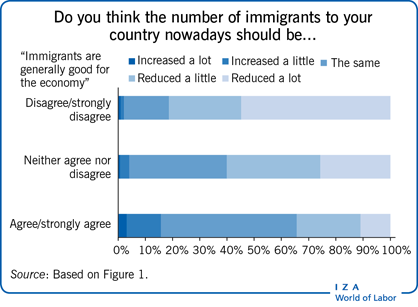
Personal characteristics of survey respondents and immigrant groups significantly influence attitudes toward immigration and immigrants.
Sociopsychological factors, such as issues related to ethnic/cultural identity, play a substantially more important role than economic concerns in driving anti-immigration attitudes.
Cons
Designing surveys that allow for cross-country comparisons for countries with different immigration experiences and legal structures is challenging.
Researchers’ current understanding of the inter-play between micro-, meso-, and macro-level factors remains limited.
To identify and disentangle the various causal channels that shape public attitudes toward immigration more research is needed.
The role of macro-level institutional and sociopolitical forces in shaping public attitudes has been largely ignored.