Elevator pitch
The recent rise of populism in advanced economies reveals major voter discontent. To effectively respond to voters’ grievances, researchers and policymakers need to understand their drivers. Recent empirical research shows that these drivers include both long-term trends (job polarization due to automation and globalization) and the rise in unemployment due to the recent global financial crisis. These factors have undermined public trust in the political establishment and have contributed to increased governmental representation for anti-establishment parties.
Key findings
Pros
Technological change and globalization create labor market effects that feed populist discourse.
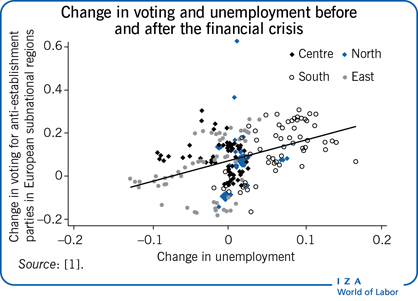
Voting for populist parties is strongly related to the increase in unemployment due to the global financial crisis.
Rising regional unemployment is likely to increase populist appeal not only among those who have lost jobs but also among those who see diminished future opportunities.
Cons
The recent rise of populism may also be driven by other factors such as cultural backlash, identity, and the spread of social media.
There is only limited evidence on recent populists’ performance once in power.
So far, there is no evidence that populists deliver on their electoral promises to restore fairness and bring back inclusive economic growth.