Elevator pitch
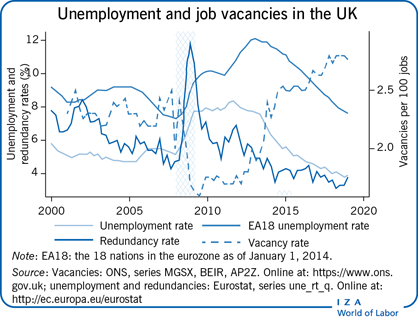
Experiences during the Great Recession support the view that the UK labor market is relatively flexible. Unemployment rose less and recovered faster than in most other European economies. However, this success has been accompanied by a stagnation of productivity and wages; an open question is whether this represents a cyclical phenomenon or a structural problem. In addition, the effects of the planned exit of the UK from the EU (Brexit), which is quite possibly the greatest current threat to the stability of the UK labor market, are not yet visible in labor market statistics.
Key findings
Pros
The UK labor market suffered less and recovered better from the Great Recession than most other EU countries, with unemployment now below its pre-2008 recession level.
While wage inequality was increasing until about the year 2000, it has been decreasing over the last ten years.
Both non-EU and EU immigrants had higher unemployment rates than UK-born workers before the Great Recession, but both groups have fared relatively better since 2008, and the gap with UK-born workers is now close to zero.
The female–male median hourly earnings ratio has been rising over time and now slightly exceeds 90%.
Cons
After the 2008 recession, labor productivity still has not recovered to its pre-recession growth rate.
Real mean and median weekly and hourly earnings remain below their pre-recession levels.
The UK’s exit from the EU is likely to have large effects on its labor market but these effects are not yet visible in the statistics.