Elevator pitch
Youth participation in extracurricular activities is associated with a variety of benefits, ranging from higher concurrent academic performance to better labor market outcomes. In particular, these activities provide avenues through which youth can develop the interpersonal and leadership skills that are crucial to succeed as a manager. A lack of opportunity to participate in extracurricular activities for many youths, particularly those from lower-income backgrounds, may have negative consequences for developing the next generation of managers and business leaders.
Key findings
Pros
Developing social skills during youth can pay dividends later during an individual’s career.
Strong social skills are important for performing in managerial occupations.
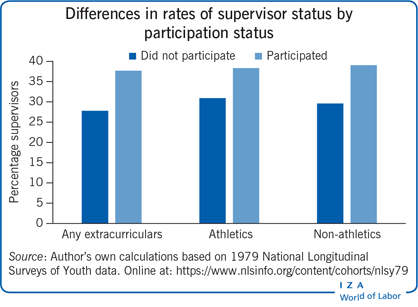
Participation in extracurricular activities during secondary school is associated with greater sociability and leads to a higher likelihood of holding supervisory responsibilities later in life.
Cons
Research has not clearly established a causal link between extracurricular activities and development of social skills.
It is not clear which activities best develop social skills.
Little is known about the relative impact of participation in extracurricular activities at different ages.