Elevator pitch
Acceptance of one’s gender identity and congruence between one’s gender identity and outward appearance are associated with less adverse mental health symptoms, and greater life and job satisfaction. However, trans people are subject to human rights violations, hate crimes, and experience higher unemployment and poverty than the general population. Trans people often feel that they are citizens who are not allowed to be themselves and practice their authentic identity. Many biased treatments of trans people could be attenuated if legal protections and inclusive workplace practices were in place.
Key findings
Pros
Acceptance of one’s trans identity is related to personal growth and resilience.
During and after transitioning, trans people experience better mental health, and greater life and job satisfaction than before transitioning.
Supportive workplace environments are related to greater disclosure of a trans identity, job satisfaction, affective commitment, and lower job anxiety.
Becoming a man is related to a small rise in earnings.
Trans employees, after having reached the point of passing, do not generally experience the bullying and harassment to which they were subjected before transitioning.
Cons
Trans people are exposed to extremely high levels of violent assault (and even murder) just for being who they are.
Trans people face higher poverty and homelessness, higher unemployment, and lower incomes as compared to non-trans people.
Around half of the EU member states require by law that trans people undergo sex reassignment surgery before their gender identity is officially recognized.
More than a third of the US states do not prohibit gender identity discrimination at work.
Becoming a woman is related to a fall in earnings.
Author's main message
Although transitioning is suggested to be a liberating process that positively affects mental health as well as life and job satisfaction, trans people regularly lack societal validation and are subject to multifaceted exclusions. Trans people should be able to change gender identification on official documents without having to undergo sex reassignment surgery. This policy would minimize employment and societal exclusions for those who are not keen, ready, or financially able to undergo such a surgical procedure. Explicit legal employment protections against discrimination on the grounds of gender identity should become mandatory.
Motivation
In the EU and the US there is a growing population of trans people who start their transition in order to shape a sense of authentic identity. Greater progress in the gender transition process is related to fewer mental health problems as well as greater life and job satisfaction [1], [2], [3]. Feelings of relief and personal progress after transition are referred to by trans employees, with many utilizing expressions such as “fulfilling,” “free,” and “empowering” to evaluate their post-transition emotional condition [2], [3]. However, due to transphobia, trans people are exposed to extremely high levels of bias [4]. Trans people often feel that they are not what they say they are; they are what their identification (ID) documents at birth say they are [4]. Due to lack of acceptance, a high incidence of harassment, and significant levels of employment exclusion, trans people are more likely to be affected by worse mental health problems and poverty than the general population [1], [3].
Discussion of pros and cons
Mental health, life, and job satisfaction
Trans people have a gender identity that differs from their assigned sex; this differentiates them from so-called cis people [3]. People with gender dysphoria suffer from feelings of psychological discomfort related to their biological sex and their belief that they belong to the opposite sex and gender [1], [3]. Trans people who align their inner gender identities with their outward appearance are found to experience a significant relief from gender dysphoria [2], [3]. This process, called transitioning, is found to be related to reduced depression and anxiety symptomatology as well as less psychological distress [2], [3]. A current review that looks at 38 cross-sectional and longitudinal studies on trans people indicates that levels of psychopathology and psychiatric disorders reduce with transitioning and, in many cases, reach normative values [3]. Positivity toward life, extraversion, the ability to cope with stress, and optimism about the future are all positively affected by transitioning; these factors all shape one’s mental health status [1], [3].
The main benefits trans people associate with being trans and accepting their gender identity are: personal growth and resiliency, improvements in their relationships with others, and being inspired to engage in social justice causes [5]. Transitioning is found to be related to greater life satisfaction [1], [2], [6]. This pattern is attributed to the factors that shape one’s life satisfaction, such as body satisfaction, appearance, self-esteem, identity and interpersonal functioning, achievements in life, spirituality, and social relationships, which are found to be positively affected by transitioning [1], [2], [3], [5], [6].
In addition, transitioning is found to be positively associated with job satisfaction [1], [2], [7]. Transitioning is related to better communication and negotiation skills, better self-organizational skills, and an innovative, constructive approach to problem-solving [1], [2], [7]. Workplace colleagues find that after transition, trans people are more loyal, helpful, productive, more approachable, and more gregarious [1], [7]. From a labor economics point of view, it is suggested that due to transitioning, the aforementioned core productivity traits may enhance trans employees’ job satisfaction [1]. Being open about one’s trans identity and coming closer to a desired outward appearance that matches one’s gender identity relieves the stresses of having to constantly hide who one is; in turn, this may promote genuine and satisfactory relationships with co-workers and supervisors [1], [7]. Approaching (transitioning to) the desired sex may allow trans employees to focus and enjoy their work more [1], [7]. Traits such as optimism, happiness, internal control, and self-esteem coming from transitioning could enable trans employees to overcome challenges at work, and to perceive their job as more fulfilling and satisfying [1]. A positive mood might induce trans people to spend more of their time on more creative tasks, and positive emotions might influence the capacity for innovation, thereby improving performance and workplace evaluations [1]. Moreover, after having reached the point of passing—the point at which a trans person is correctly recognized as the gender that they identify as, and, additionally, not identified as trans by others—trans people typically do not experience the bullying and harassment to which they were subjected before, further positively affecting their job satisfaction [1], [6].
Among trans employees, a trans-supportive workplace climate is related to greater disclosure of identity in the workplace, job satisfaction and affective commitment, and lower job anxiety [1], [2], [4], [6], [7]. Trans people might become most happy and productive if they can contribute their time and energy to societies and workplaces that accept their existence and welcome their labor contributions [1].
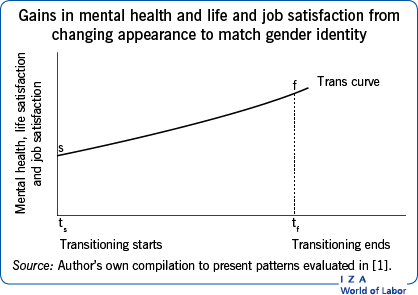
The trans curve
As seen in the Illustration, the trans curve (TC) presents positive relationships between transitioning, mental health, life satisfaction, and job satisfaction [1]. Point ts, on the horizontal axis, denotes the time or stage at which transitioning starts. Point tf, on the horizontal axis, denotes the time or stage at which transition ends. The vertical axis presents the mental health (MH), life satisfaction (LS), and job satisfaction (JS) constructs. As informed from the international literature [1], [2], [3], [5], [6], TC demonstrates that trans people experience positive MH, LS, and JS advancement during transitioning (as represented by the comparison between point s and points lying in the s to f section on TC) and as a result of transitioning (as represented by the comparison between points s and f on TC). The MH, LS, and JS constructs consist of different indicators, and different scales are used for quantification [1]. The three corresponding curves should not coincide in practice, although all are characterized by a positive slope.
Acceptance of one’s trans identity is supposed to either precede or coincide with the initiation of transitioning. Based on empirical observations, positive MH, LS, and JS advancement appears even at the stage of acceptance of one’s trans identity [1], [5]. What constitutes the end of the transitioning process is subjective, and varies from person to person [1]. The end of transitioning is a broad concept, which might entail alignment between gender identity and outward appearance, with or without medical/surgical interventions, and/or changes in identity documents, and/or successful passing [1].
Attention should be paid to the range of factors affecting the information represented by the horizontal and vertical axes in the Illustration on page one. Factors affecting the acceptance of one’s trans identity and the duration of transitioning (horizontal axis) are, among others: inner and personal decisions and desires; family, peers, school, workplace, network, and institutional support; and financial budgets [1]. Factors affecting trans people’s MH, LS, and JS (vertical axis), apart from the usual demographic and socio-economic characteristics, should include, among others, the degree of inclusiveness in societies and workplaces; stigma prevention programs; coping intervention strategies; anti-discrimination policies; positive actions; accessible and affordable transitioning resources; hormone therapy; surgical treatments; high- quality surgical techniques; adequate preparation and mental health support before and during transitioning; and proper follow-up care [1].
At the same time, factors negatively affecting trans people’s MH, LS, and JS are found to be societal marginalization; family rejection; violations of human and political rights in health care, employment, housing and legal systems; gendered spaces; and internalization of stigma[1].
It is expected that reciprocal effects between MH, LS, and JS exist [1]. The causal relationships among MH, LS, and JS therefore represent an enduring question in the social sciences. In all cases, empirical investigation is required to evaluate how the aforementioned factors mediate and moderate the relationships which are present.
Transitioning and earnings: The case of trans men
In the literature, two studies have focused on trans men and earnings. Some very small positive effects are observed. The first study shows that becoming a trans man in the US brings a small increase in hourly earnings of about 1.5% [6]. The second study, utilizing Dutch data, shows that becoming a trans man increases annual earnings by approximately 7% [7]. However, the increase is statistically insignificant. Both studies suggest that becoming a man might bring an increase in respect and authority that could affect job rewards [6], [7].
Biases against trans people
Trans people challenge the rigid concept of gender since their gender identity does not reflect the societal gender norms associated with the sex assigned at birth. When social structures and expectations require that individuals who are born male reflect masculine attributes and female reflect feminine attributes then such an identity could result in discriminatory treatments. Myths about transition regrets dominate the media and society. Misrepresentation of scientific results on transitioning boost transphobia, and creates a biased environment against trans people. Several studies have shown that marginalized and vulnerable trans people suffer from depression, anxiety, and self-harm; they experience suicidal thoughts related to the lack of societal validation, rejection from family and social environments, years of transphobic experiences, and lack of appropriate health service provision [4][10].
Recent studies indicate that in the UK, trans people are less likely to have a paid job and more likely to earn less than cis people [8]. In the US, trans people have lower incomes and are more likely to be in poverty, unemployed or working part-time, when compared with cis men [9].
The workplace is one of the most likely places for trans discrimination to occur. Lack of workplace help, understanding, and support for trans people can lead to biased treatment [4], [10]. Trans employees are reported as having been outed by others, being deliberately called by a former name or gender pronoun, being fired, or denied a job, physically threatened, or emotionally abused [4], [10].
In the UK, a recent study found a strong prejudice amongst employers towards trans men and women, with one in three employers admitting they are ‘less likely’ to hire trans employee and nearly half (43%) unsure if they would recruit a trans employee [11].
The biased climate in relation to trans people in the UK, US and the EU pervades multiple facets of life, including education, health care, and access to credit [8], [9], [10], [11]. As a result, trans people’s integration and well-being suffer [1], [8], [9]. These patterns highlight how trans people’s employment life is negatively affected by transphobic actions. Societal discrimination prevents trans people from being able to enjoy the right to respect for their private lives, which encompasses the right to express one’s identity in all areas of life [8], [9], [10], [11].
Transitioning and earnings: The case of trans women
Transitioning is found to negatively affect earnings for trans women. A study that utilizes US data suggests that becoming a trans woman brings a reduction in hourly earnings of about 32% [6]. Also, an EU study, based on Dutch data, shows a reduction in annual earnings, on the order of 23% [7]. This finding is in line with qualitative evaluations that show that trans women’s transitions often bring a loss of masculinity that entails loss of authority and leadership, and initiates a new period of harassment and biased treatment [6], [7]. On the other hand, as previously presented, becoming a trans man might positively affect earnings. A masculine identity might entail an increase in dominance and leadership, traits that are rewarded in the labor market [6], [7].
Identity documents
Trans individuals experience employment challenges and severe exclusions when they are unable to obtain identity documents that reflect their gender identity. Biased treatments are observed during selection and promotion processes when people dress and live as one sex even though they were born as another [10]. Unfortunately, in many countries, trans people can change their ID documents only after undergoing sex reassignment surgery [1]. However, a large part of the trans community is not keen on surgically reassigning their sex. They are happy to live, experience, and celebrate their gender identity without surgical procedures [1]. Having to choose between sex recognition and potential sterilization, which occurs in sex reassignment surgeries that include genital reconstruction, is a human rights violation.
Workplace positive actions and outcomes
In the UK, in 2015 the Government Equalities Office released a workplace guide for employers on recruiting and retaining trans staff [12]. The aim of the guide was to build awareness and understanding of trans issues by establishing support structures for trans people by helping employers comply with the law and providing them with practical advice on the recruitment and retention of trans employees and potential employees [12]. The guide sets out good practice in relation to equality monitoring and human resources procedures, relating to inductions and ways to support staff members who are planning to transition.
A study found that firms which have implemented the Government Equalities Office workplace guide have informed human resources strategies, affected corporate profiles and staff organizational behaviors, created a more inclusive workplace culture, and addressed LGBTIQ+ business and trans staff members’ needs [12]. Moreover, the study found that trans people’s self-esteem and self-respect were enhanced by policymakers’ positive actions to promote gender identity inclusivity in the workplace. In addition, due to these actions trans people felt more accepted, valued and trusted by the government.
The study concluded that when firms utilize policymakers’ positive workplace policies related to gender identity diversity, they may be able to realize positive organizational outcomes in their workplaces. Moreover, if inclusivity policies are perceived to be a recognition of trans people’s worth this may be internalized, resulting in positive selfevaluations [12].
Limitations and gaps
Several problems lie in the continuing lack of information about trans issues. The public, media, policymakers, and employers lump trans issues in with sexual orientation, and this has nothing to do with gender identity. A trans person may be straight, lesbian, gay, or bisexual [1]. The experiences, the nature of the bias, and the corresponding policy actions differ between trans people and sexual orientation minoritized groups. There is a need for education on the aforementioned differences, and on the approaches required to deal with the needs of each population group. Also, the interaction between gender identity and sexual orientation and its effect on people’s lives requires additional focus and research-informed policies.
Researchers often treat trans people and gender non-conforming people as belonging in the same category. However, each category captures a different population group [1]. Gender non-conforming people are those who do not identify as either male or female all the time. And there are lots of subsections in the gender non-conforming community—people might be, for instance, gender fluid, bi-gender, or agender. Grouping all these people into a single category introduces bias. Research studies should clarify their target population, and topical questions should capture the distinction between trans and gender non-conforming people.
Furthermore, representative data sets on trans people rarely exist. The lack of representative data sets means that robust research is rarely conducted. Data sets that enable comparisons before, during, and after transitioning could shed light on the dynamics of employment rates, earnings, workplace commitments, and evaluations. In addition, comparisons between trans and cis people would enable researchers to evaluate inequality and discriminatory patterns in relation to earnings and employment outcomes.
Summary and policy advice
Policymakers should consider the establishment of programs that tackle minority stress, exclusion, and discrimination [1], [12]. If people are allowed to transition and smoothly integrate into society without harassment, they might turn out better adjusted [1]. For trans people to have better access to job vacancies, to cope smoothly in employment, and to integrate into society, they should be able to change their sex on government ID documents without having to undergo sex reassignment surgery. Governments should approve legislation that would cancel the long-standing and cruel requirement that trans people provide proof of sex reassignment surgery before being able to legally change their sex [12]. In recent years, Malta, Ireland, and Norway allowed trans people to change their sex by simply notifying the authorities, without any medical or government intervention. In addition, trans and gender non-conforming people should be protected from gender identity discrimination in the labor market by the government.
Anti-discrimination legislation and inclusive workplace environments are believed to reduce trans people’s unemployment, income inequality, and poverty rates [12]. A progressive equality policy can enhance a company’s reputation and improve employees’ performance and productivity [12]. To improve employees’ work-related attitudes and experiences, firms might implement training programs that encourage individuals to be their true selves at work and simultaneously create work environments that promote greater acceptance of employees from different identity categories through awareness and inclusion initiatives [12].
Gender identity inclusion can be achieved through diversity management, training on the recruitment and retention of trans people to enable firms to secure the best possible applicants regardless of their gender identity, inclusiveness on firms’ websites and brands, a transitioning at work policy to support people intending to go through gender transition, and an official support system for employees wishing to disclose their trans status [12]. Mentoring schemes, and counselling support could positively affect trans employees’ workplace experiences [12]. Effective retention strategies addressing trans employees’ needs would avoid costs to the organization resulting from job dissatisfaction, formal complaints, resignations, and tribunals.
Firms that understand the business benefits of an inclusive workforce will recognize the need to respond to the differing requirements of all their employees [12]. Firms should make it clear that there will be no concessions for managers, colleagues, or customers who act in a biased manner, as these behaviors reflect on the company [12]. Firms should not refuse to hire and promote trans or gender non-conforming people, or refuse to step in if colleagues or customers are harassing an employee for being trans, nor should they fire trans people for being themselves. Firms should ensure that human resources departments have knowledge and awareness of trans-related issues [12]. A cooperative social dialogue between policymakers, employers, and trans employee representatives would offer opportunities to develop human resources policies at the organizational level to confront and eliminate trans bias in workplaces [1], [12].
Finally, technological advancements such as mobile health applications have been found to increase the physical and mental health status for trans people, especially during challenging periods such as during the COVID-19 pandemic [13]. One of the most notable advantages of mobile health applications are the access to healthcare services which they provide for trans people. If technological advancements can reduce physical and mental health symptoms, then their potential use for minoritized people and during periods of unprecedented stress should be considered [13]. The notion of an information society is converging with that of an inclusive society where access to, and use of, technology should be considered as a potential tool for fostering inclusive policies for minoritized peoples’ well-being [13]. Apart from technology-oriented opportunities, actions to minimize stigma and exclusions against trans people in families, schools, and services should be considered, which in turn could reduce the factors which negatively affect trans people’s development and progression in the workplace.
Acknowledgments
The author thanks two anonymous referees and the IZA World of Labor editors for many helpful suggestions on earlier drafts. Previous work of the author contains a larger number of background references for the material presented here and has been used intensively in all major parts of this article [1] and [12]. Version 2 of this article adds new arguments e.g. on earnings effects and workplace positive actions. It adds new further readings and key references [8], [9], [11], [12], and [13].
Competing interests
The IZA World of Labor project is committed to the IZA Guiding Principles of Research Integrity. The author declares to have observed these principles.
© Nick Drydakis
Key definitions for understanding gender identity
Cis refers to people who have a gender identity that matches the sex that they were assigned at birth.
Discrimination against trans people, captures, amongst other concepts, the unequal treatment of trans people on the basis of their group membership rather than on the basis of their individual qualities.
Gender is the state of being a man or woman, and is typically used with reference to social and cultural differences rather than to sex.
Gender dysphoria refers to trans people’s feelings of distress because of the mismatch between their sex and their gender identity.
Gender identity is defined as an internal and personal conception of oneself as a man or woman.
Gender non-conforming is a gender expression by a person that does not match masculine and feminine gender norms.
Passing refers to the transitioning stage where a trans person can move through the world without anyone suspecting that they are trans.
Sex refers to the biological differences between men and women.
Trans refers to people who have a gender identity that differs from their assigned sex.
Trans men refers to women who become men.
Trans women refers to men who become women.
Transitioning refers to the process of changing outward appearances to accord with gender identity. Transitioning might, but does not always, involve medical treatment.
Transphobia refers to dislike of and/or prejudice against trans people.