Elevator pitch
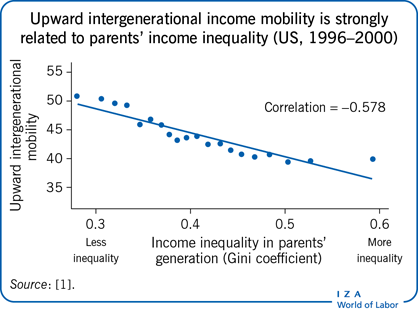
Income inequality has been on the rise in many countries. Is this bad? One way to decide is to look at the degree of change in incomes across generations (intergenerational mobility) and, more generally, at the extent to which income differences among individuals are traceable to their social origins. Inequalities that reflect factors largely out of an individual’s control—such as parents’ education, local schools, and communities—require attention in order to reduce income inequality. Evidence shows a negative association between income inequality and intergenerational mobility, and a positive relationship between mobility and economic performance.
Key findings
Pros
Promoting greater intergenerational mobility may increase equality of opportunity.
Policies that foster intergenerational mobility may incentivize human capital investments and productive effort.
Youth communities (school and neighbors) play a role in determining inequality mostly in the short term.
Even if a large part of intergenerational transmission of income is due to genetic factors, policies may still have an effect in reducing inequality.
Within countries, more mobile regions have better economic performance.
Cons
Income differences reflect individual efforts and redistributive policies could curb individual incentives.
Growing income inequality may increase social segmentation and reduce equality of opportunities.
Income differences between individuals in a generation reflect to a significant extent differences between their parents.
A non-negligible share of intergenerational transmission is ascribable to genetic factors.
Countries or regions with high income inequality tend to have low intergenerational mobility.