Elevator pitch
In today’s globalized world, people are increasingly mobile and often need to communicate across different languages. Learning a new language is an investment in human capital. Migrants must learn the language of their destination country, but even non-migrants must often learn other languages if their work involves communicating with foreigners. Economic studies have shown that fluency in a dominant language is important to economic success and increases economic efficiency. However, maintaining linguistic diversity also has value since language is also an expression of people’s culture.
Key findings
Pros
Economic well-being is enhanced when members of a group communicate in the same language.
Learning the dominant language is an investment in human capital.
There are important financial benefits to members of linguistic minorities who learn the dominant language; those who use their native language do not experience such benefits in the labor market.
Because of externalities in the use of a common language, letting individuals pursue their self-interest may not lead to optimal outcomes.
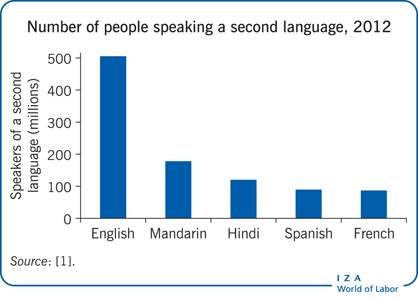
The trend toward English as a common second language has some advantages and cannot be reversed.
Cons
Linguistic diversity has value, although some of it is non-pecuniary.
Because of the link between culture and language, the more languages that can be accommodated, the greater the welfare.
Knowing other languages can bring benefits, and linguistic diversity can increase the number and type of goods available.
Public support for a minority language is an indication that people value it and are willing to take action to maintain it.
While there has been a tendency toward language convergence globally, there is also a desire to maintain diversity.