Elevator pitch
Addressing unauthorized immigration is controversial. Countries have adopted a variety of legalization programs, ranging from temporary visa programs to naturalization. Research in the US focused on past amnesty programs finds improved labor market outcomes for newly legalized immigrants. Findings are more mixed for European countries. Studies suggest that regularization of undocumented immigrants can result in increased use of public benefits and reduced formal labor market participation. Despite widespread disagreement, legalization is widely used in practice.
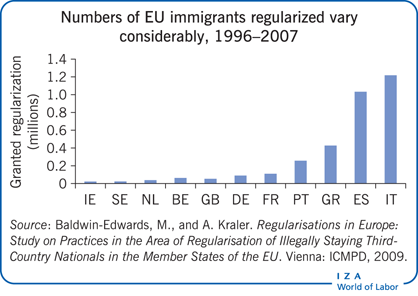
Key findings
Pros
Legalization allows previously undocumented immigrants to come out of the shadows, reducing risks of workplace exploitation.
Better job matches may result, potentially increasing wages, non-pecuniary benefits, and returns to skills, education, and language ability.
Legalization can address some humanitarian and political concerns by allowing access to social services, higher education, and equal protection under the law.
Tax revenues may rise as more immigrants, particularly the high-skilled, start paying taxes, and those already paying taxes contribute more as their incomes rise.
Legalization may result in increased investment in education and health.
Cons
Legalization programs may attract more illegal immigration.
Legalization may have negative consequences for workers who compete with newly regularized immigrants, through increased competition for jobs and lower wages.
Firms may see a reduction in the responsiveness of the available workforce following legalization.
Government budgets may be negatively affected through increased spending on social services, especially if newly legalized immigrants are relatively poor.
Issues of fairness make legalization a contentious tool for dealing with undocumented immigrants.