Elevator pitch
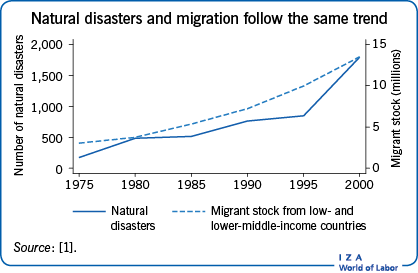
The relationship between climatic shocks, climate related disasters, and migration has received increasing attention in recent years and is quite controversial. One view suggests that climate change and its associated natural disasters increase migration. An alternative view suggests that climate change may only have marginal effects on migration. Knowing whether climate change and natural disasters lead to more migration is crucial to better understand the different channels of transmission between climatic shocks and migration and to formulate evidence-based policy recommendations for the efficient management of the consequences of natural disasters.
Key findings
Pros
Migration can help people cope with the adverse effects of climatic shocks by providing them with new opportunities and resources.
Remittances increase after disasters and play an important role in mitigating the adverse effects of climatic shocks and natural disasters.
Climatic factors, such as hurricanes, floods, droughts, or rainfall and temperature variations, may increase international migration through their effect on internal migration.
Agricultural productivity represents one of the pathways that can explain the relationship between climatic shocks and migration.
Public intervention both before and after disasters helps build resilience and can explain why migration responses differ depending on the types of shocks.
Cons
The migration response to disasters depends on the nature of the shock (slow vs rapid onset events), its severity, and the vulnerability of the affected people.
Due to liquidity constraints, poor people might not be able to migrate in the aftermath of climatic shocks.
In developing countries, international migration due to disasters may be driven by highly educated people, which may foster brain drain in a vulnerable context.