Discurso de ascensor
Artificial intelligence (AI) has streamlined processes, improved workforce allocation, and created new jobs to meet the needs of digitalization and automation. Individuals with AI capital experience greater employment opportunities and higher wages, particularly in high-skilled roles and large firms. Training in AI helps reduce gender-based digital disparities, empowers individuals, and enhances their employability. Policymakers should promote inclusive AI development policies to prevent widening AI-related divides and unemployment, and to ensure equitable opportunities.
Hallazgos clave
Pros
Investments in education and skills related to AI have boosted employment, particularly in high-skilled occupations.
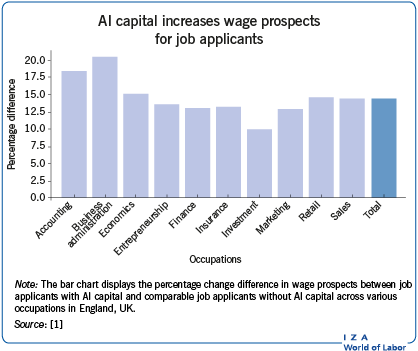
AI adoption has led to higher demand for AI-related skills and wage premiums, especially in high-skilled occupations.
AI has increased employee productivity for less-experienced and lower-skilled employees.
AI helps industries weather economic downturns by stabilizing employment levels.
AI enhances job quality for historically disadvantaged groups by reducing reliance on physical strength and promoting cognitive skills.
Contras
AI increases job displacement risks for low-skilled, routine employees, widening the gap between high- and low-skilled employees.
AI-investing firms favor highly educated employees, reducing non-degree roles and some non-technical jobs.
AI might worsen income inequality, especially impacting low-skilled employees.
Employees’ distrust of workplace AI stems from perceiving AI as a threat and dissatisfaction with overpromised AI capabilities.
There are concerns about AI's ethics and transparency, especially in decision-making processes.