Elevator pitch
Policymakers rely on entrepreneurs to create jobs, provide incomes, innovate, pay taxes to support public revenues, create competition in industries, and much more. Due to its highly heterogeneous nature, the choice of entrepreneurship measures is critically important, impacting the diagnosis, analysis, projection, and understanding of potential and existing policy. Some key aspects to measure include the how (self-employment, new firm formation), why (necessity, opportunity), and what (growth). As such, gaining better insight into the challenges of measuring entrepreneurship is a necessary and productive investment for policymakers.
Key findings
Pros
Various measures can help policymakers capture different dimensions related to entrepreneurship.
More precise measurement options can help target specific types of entrepreneurship or outcomes, such as high growth entrepreneurship.
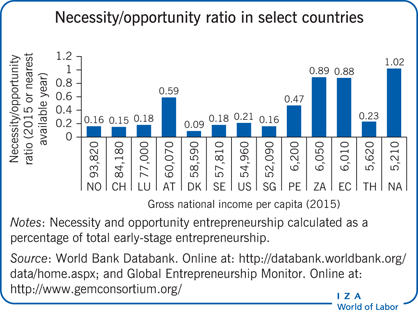
Comparing multiple measures of entrepreneurship, such as necessity and opportunity entrepreneurship, can be useful.
Different measures, like employment-based or accounting-based measures, can be used to evaluate growth entrepreneurship.
Cons
Measures for new firm formation likely underestimate the entrepreneurial activity in certain places, especially in low-income countries.
There are large gaps in data availability for many countries, especially low-income countries.
Different reporting and accounting standards limit the comparability of firm-level data across countries.
While it is possible to assess entrepreneurs’ intentions, it is harder to measure growth.
A lack of comparable measures hinders research on growth entrepreneurship.